🦠 What Is Mold?
Mold is a type of fungus that thrives in damp environments and can cause health risks indoors.
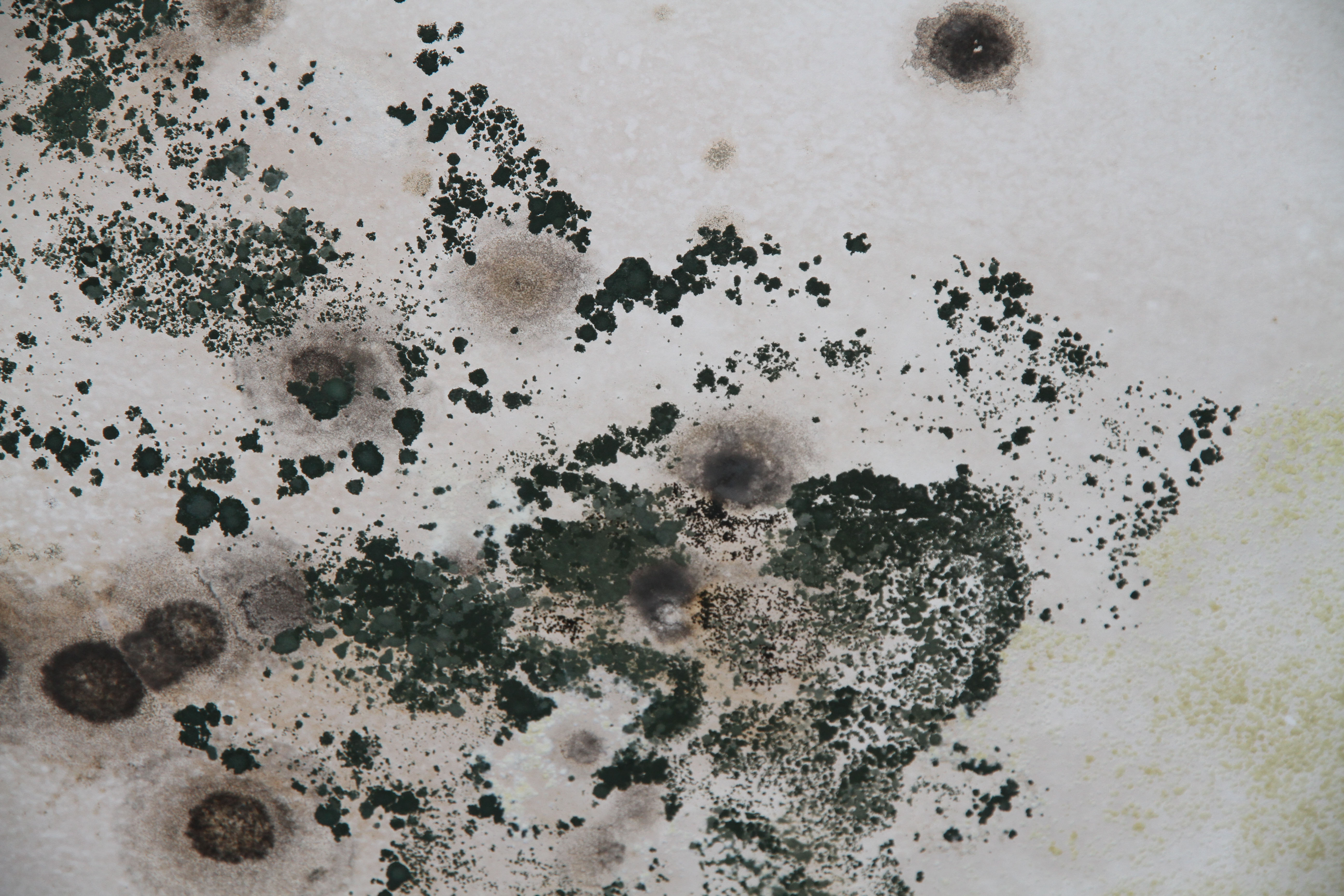
Mold grows in multicellular structures called hyphae, forming colonies on moist surfaces like drywall, carpet, and wood.
It reproduces through airborne spores and can grow quickly under the right conditions—within 24 to 48 hours.
While mold helps decompose organic matter in nature, indoors it can cause health issues, especially certain types like Stachybotrys chartarum (black mold).
Mold inspection and remediation help protect your home and health from hidden growth.
Mold is a type of fungus that grows in multicellular structures known as hyphae, forming visible patches called colonies. It thrives in environments with excess moisture, such as areas affected by leaks, flooding, or high humidity.
Mold can grow on a wide range of organic surfaces including drywall, wood, carpet, insulation, and fabric. It reproduces through tiny, lightweight spores that travel through the air and settle on damp surfaces, where new colonies can quickly form—often within 24 to 48 hours under the right conditions.
While mold plays an important role in nature by breaking down dead organic matter, its presence indoors can be harmful. Certain mold species, such as Stachybotrys chartarum (black mold), can release mycotoxins— toxic compounds known to cause respiratory issues, allergic reactions, and other health complications.
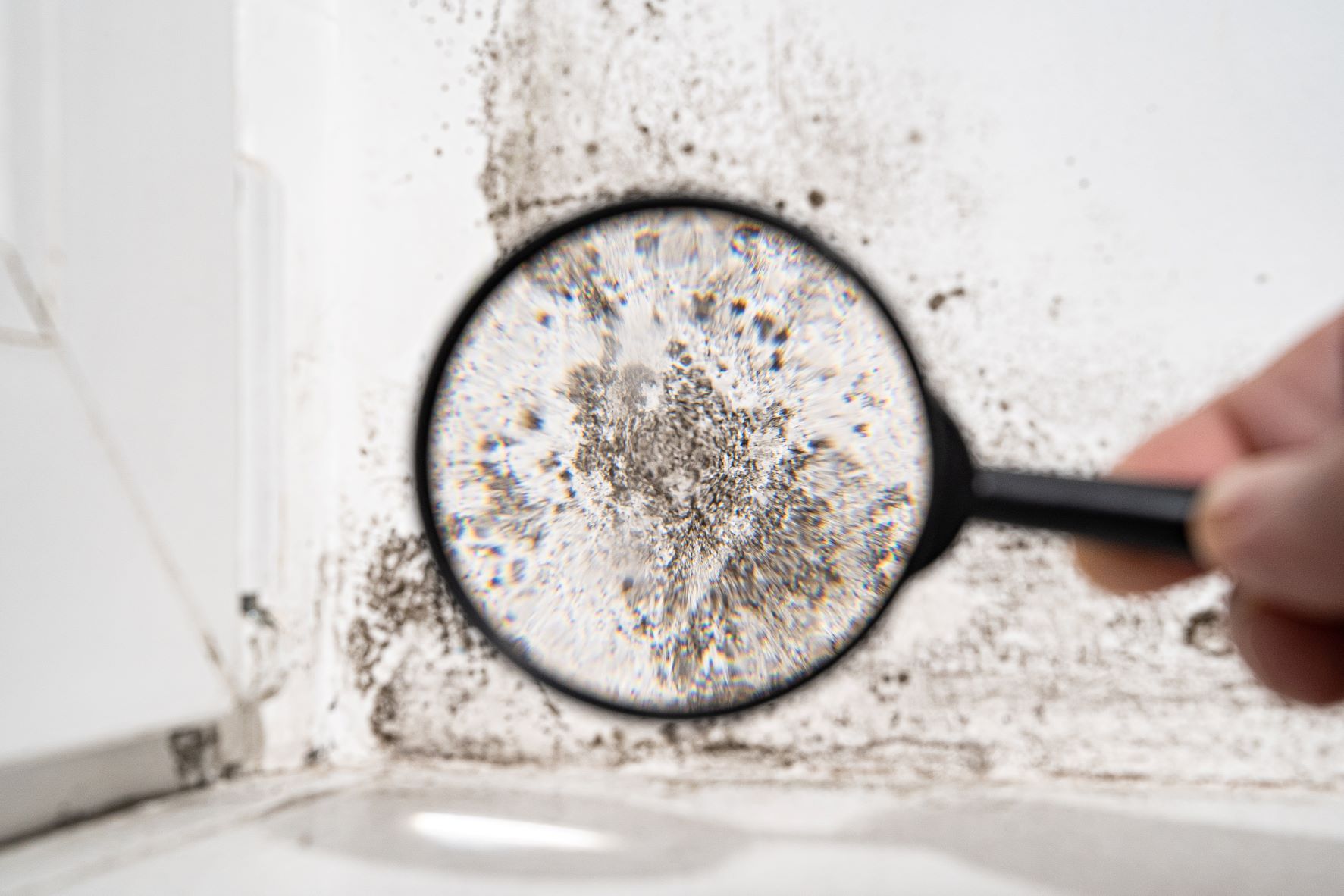
Even non-toxic mold varieties can negatively impact indoor air quality and trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals. Because mold often grows out of sight—behind walls, under flooring, or inside HVAC systems—it’s difficult to detect and remove without professional tools and expertise.
That’s why timely mold inspection, testing, and remediation are critical steps in protecting both your property and your health.

Mold growing on an indoor surface
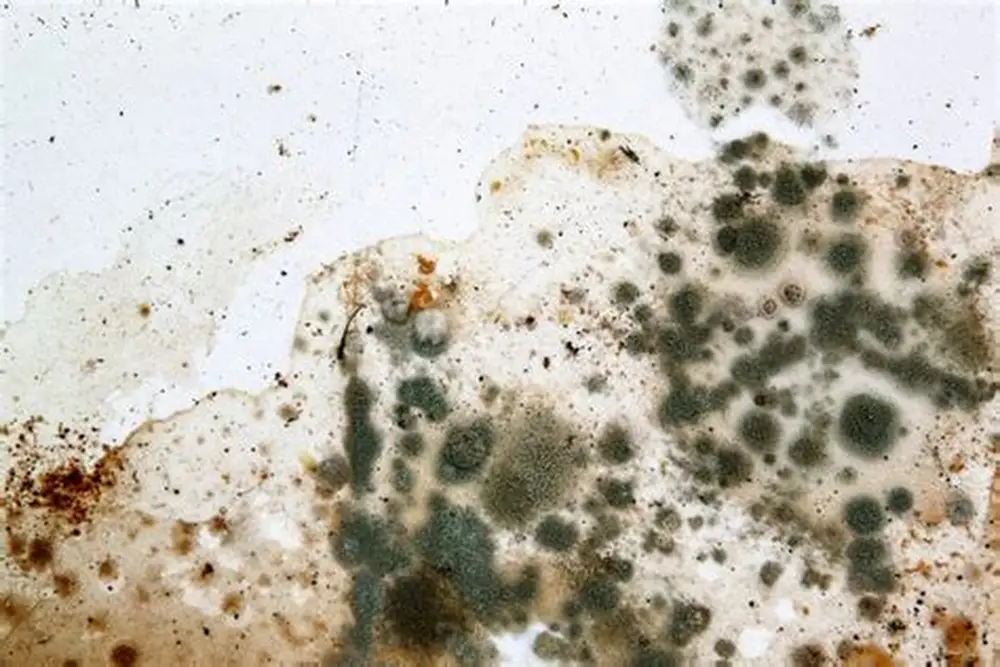
Close-up of mold spores under microscope
Types of Mold Found Indoors
Indoor mold comes in many forms. Some are common and harmless, while others can lead to serious health and structural issues. Learn about the most frequent types we encounter during inspections.
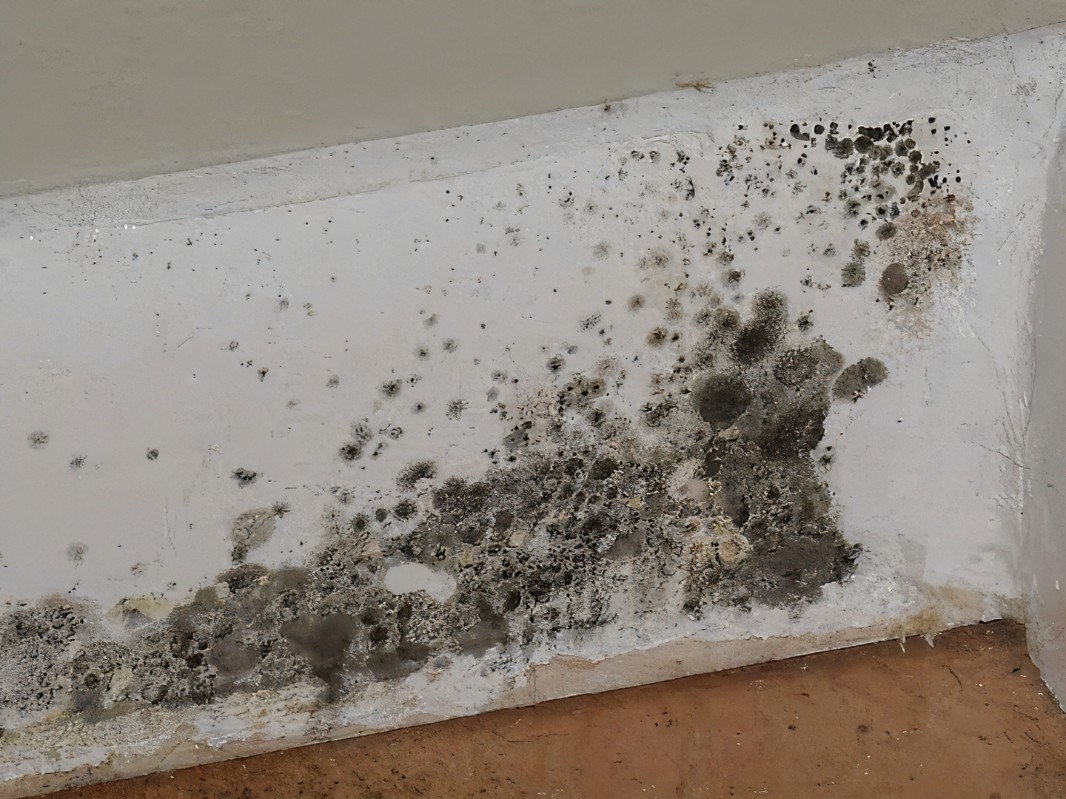

Stachybotrys (Black Mold)
Commonly known as toxic black mold, this dark mold grows on damp drywall, wood, and insulation. It can release dangerous mycotoxins and lead to severe respiratory problems.

Aspergillus
Found on dust, food, and walls, Aspergillus can cause allergic reactions and lung infections, especially in people with weakened immune systems.

Cladosporium
Appearing dark green or brown, Cladosporium often grows on fabrics and wood. It may trigger asthma symptoms and allergic reactions.
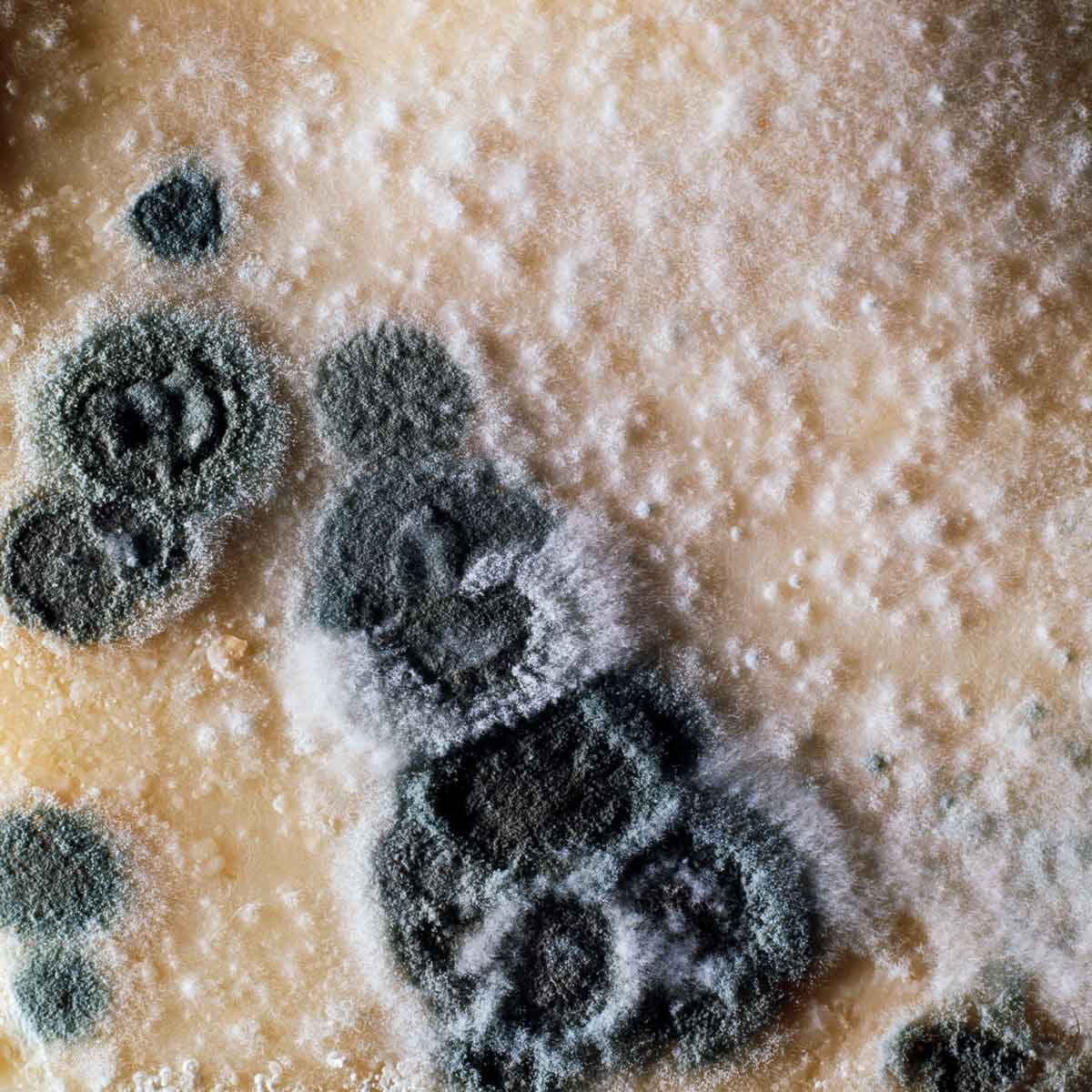
Penicillium
This fast-growing mold appears blue or green and spreads quickly on damp materials. It's known to worsen allergies and asthma.

Alternaria
Typically found in damp places like showers and sinks, Alternaria is a common allergen that can irritate the nose, mouth, and upper respiratory tract.

Fusarium
Often grows on water-damaged carpets and wallpapers. Prolonged exposure can cause infections and allergic reactions.

Family protecting themselves from mold exposure
🛑 Why Mold Is Dangerous
Mold affects indoor air quality and can lead to allergies, asthma, and other respiratory issues. Toxic mold may even cause neurological effects with long exposure. It's especially harmful to children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals.
Mold is more than just an unsightly stain on your wall—it's a serious health hazard. When mold spores are released into the air, they can be easily inhaled, affecting the lungs and respiratory system. People with asthma, allergies, or weakened immune systems are especially vulnerable to the effects of mold exposure.
Breathing in mold spores can cause a range of symptoms, including persistent coughing, sneezing, wheezing, and eye irritation. Even individuals with no history of allergies may develop sensitivities after prolonged exposure. Skin rashes and sinus congestion are also common.
One of the most dangerous types of mold is Stachybotrys chartarum, commonly referred to as black mold. This toxic mold can produce harmful mycotoxins that may cause neurological problems, chronic fatigue, and in severe cases, long-term respiratory damage. Children, elderly individuals, and those with compromised immune systems are most at risk.
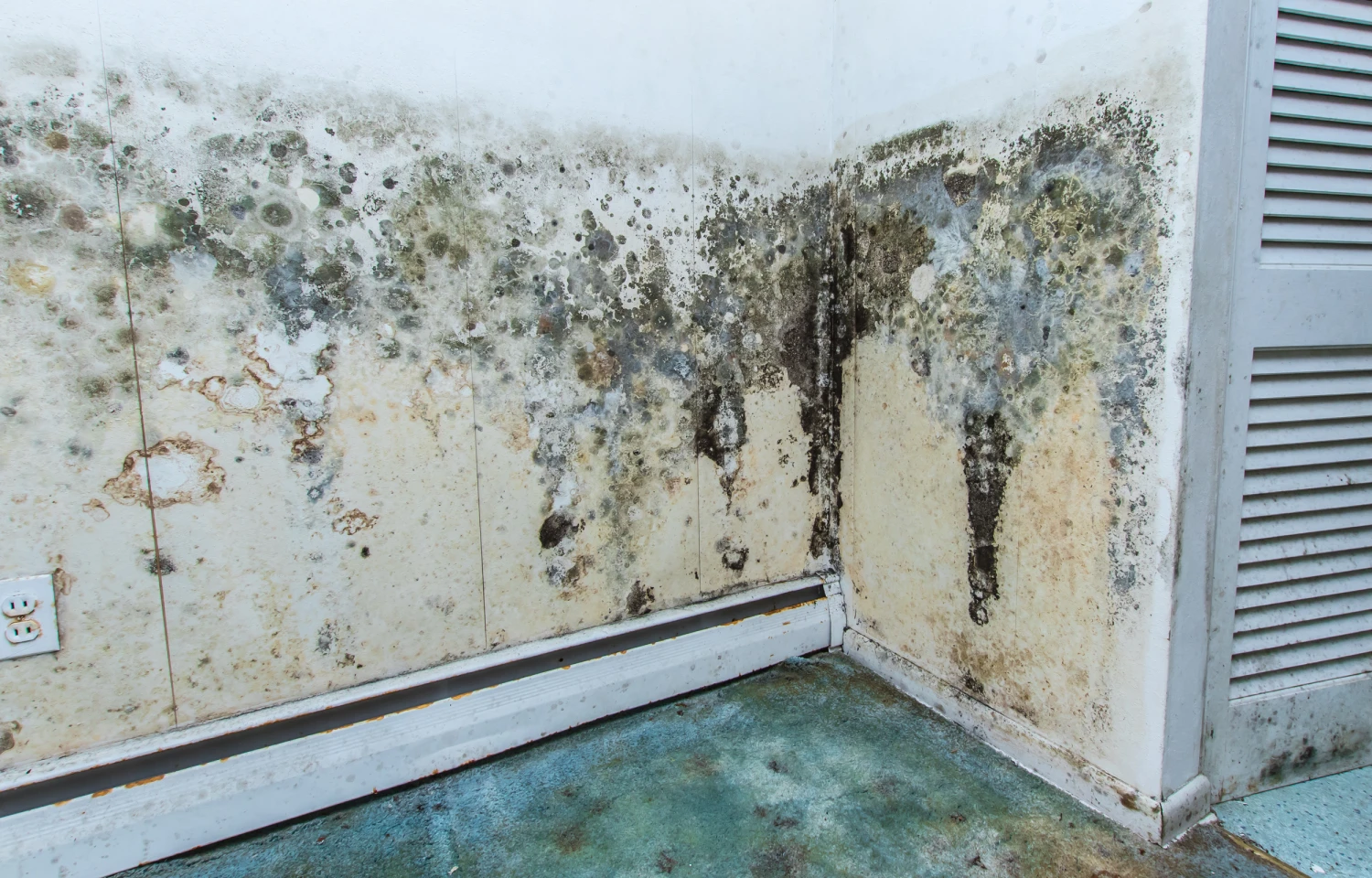
In homes with poor ventilation or a history of water damage, mold can grow undetected behind walls, under floors, and in HVAC systems. Because it's often hidden, many people continue to live with dangerous mold exposure without realizing the cause of their health issues.
Timely mold inspection, air quality testing, and professional remediation are essential steps to prevent these risks. Protecting your indoor environment from mold means protecting your health and the health of everyone who enters your home or workplace.

Lifecycle of indoor mold growth

Moisture and water leaks as primary mold sources
🌱 How Mold Grows
Mold needs moisture, organic material, and lack of sunlight to grow. Common places include basements, bathrooms, and around leaky pipes. Good ventilation and moisture control are essential to prevent mold growth.
Mold growth is primarily driven by one thing: moisture. Mold spores are always present in the air, both indoors and outdoors. However, they only become a problem when they find the right environment to settle and multiply. That environment typically includes excess moisture, organic material, and a lack of ventilation.
Common indoor sources of moisture include plumbing leaks, roof damage, flooded basements, high humidity, and poor ventilation. Once mold spores land on a damp surface—such as drywall, wood, carpet, or insulation—they begin to colonize within 24 to 48 hours.
Mold feeds on organic materials found in building materials, fabrics, and even dust. Areas with limited sunlight and stagnant air are especially vulnerable, making bathrooms, kitchens, attics, and basements prime targets for mold infestation.
HVAC systems can also contribute to mold spread. If mold grows inside air ducts or vents, spores can be distributed throughout your home, affecting multiple rooms and the health of everyone inside.
Preventing mold growth starts with moisture control. Regular inspections, quick repairs of water damage, use of dehumidifiers, and proper airflow are key steps in stopping mold before it starts. If mold does appear, it should be professionally inspected and remediated to avoid further spread and health complications.
Did You Know?
"The EPA states that all molds have the potential to cause health effects. It is crucial to eliminate sources of moisture and remove mold promptly."